when a cell does not have an electron transport chain, it uses fermentation to do what?
Jail cell Processes: Fermentation
Resources ID: BM1L6
Form Range: nine - 12
Allow'southward Get Started
How do organisms generate energy when oxygen is not available? Let'south explore how humans, bacteria, yeast, and other organisms undergo fermentation to generate energy from food in the absence of oxygen. Before you become started, don't forget to impress out your OnTRACK Biology Journal.
TEKS Standards and Student Expectations
B(four) The student knows that cells are the basic structures of all living things with specialized parts that perform specific functions and that viruses are unlike from cells. The pupil is expected to:
B(4)(B) investigate and explicate cellular processes, including homeostasis, energy conversions, transport of molecules, and synthesis of new molecules
Learning Objectives
Identify and describe the processes organisms use to release free energy from nutrient when oxygen is not available.
Depict the process human being muscle cells utilize to release energy during strenuous exercise.
Explain the benefits and the challenges of fermentation.
Compare and contrast fermentation and cellular respiration.
Compare and contrast lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation.
Essential Questions
How do organisms generate energy when oxygen is not available?
How is fermentation similar to cellular respiration and how is information technology different?
How is fermentation in yeast like to fermentation in human muscle cells and how is it dissimilar?
How practise humans utilize fermenting bacteria and yeast to generate useful products?
Vocabulary
- ATP
- Fermentation
- Glycolysis
- Glucose
- NAD+/NADH
- Pyruvate (Pyruvic Acid)
- Lactic Acid Fermentation
- Lactic Acid (Lactate)
- Alcoholic Fermentation
- Ethyl Booze (Ethanol)
Fermentation: An Introduction
Pause for a moment and take a deep breath in. Equally you do, air fills your lungs. Your lungs and bloodstream piece of work to supply your cells with plenty of oxygen to generate the energy the cells need to office. Recall, cells use oxygen to generate usable energy, or ATP, from the food nosotros eat. This is usually done through the process of cellular respiration. In cellular respiration, oxygen accepts electrons at the end of the electron transport chain where the majority of ATP is formed. Without oxygen, the electron transport chain stops generating ATP.
| When you perform strenuous exercise similar sprinting in a race, your muscles require energy production faster than your lungs and bloodstream tin deliver oxygen. Your muscles are forced to work without plenty oxygen. In these situations, your working muscles generate ATP anaerobically (i.east., without oxygen) using a procedure called fermentation. Fermentation is beneficial in that it can generate ATP quickly for working muscle cells when oxygen is scarce. |  |
Glycolysis
Fermentation is glycolysis followed past a procedure that makes it possible to proceed to produce ATP without oxygen. Klycolysis is the first series of reactions that occur during cellular respiration. G lycolysis does not crave oxygen to produce ATP.
During glycolysis, glucose is broken down into ii molecules of pyruvate (pyruvic acrid). Two ATP molecules are required, and four ATP molecules are produced, resulting in a net gain of two ATP. Electrons are besides transferred to two NAD+ molecules, forming two NADH molecules.
The following diagram summarizes glycolysis.
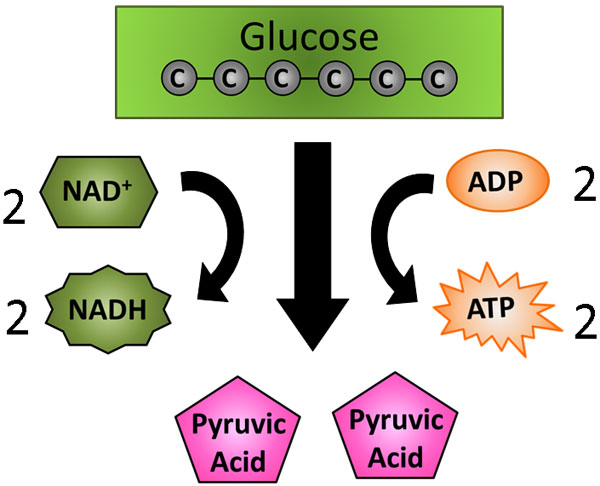
When cells generate big amounts of ATP through the process of glycolysis, they quickly use up the cell'south available NAD+ molecules. Once all available NAD+ molecules are converted to NADH,glycolysis stops producing ATP. Without oxygen, the citric acid wheel (Krebs wheel) and electron transport concatenation will non run, so at that place is nowhere for NADH molecules to eolith their electrons.
Directions: Watch What Happens When You Run Out Of Oxygen! to come across an animation showing NADH build up when a cell runs out of oxygen.
Source
Picardposer. What Happens When You lot Run Out Of Oxygen! Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=StXlo1W3Gvg&feature=youtu.exist
As you can encounter, without oxygen, the electron carriers in the electron ship chain cannot have electrons from NADH. No NADH gets converted to NAD+. Without NAD+, cells cannot keep going through glycolysis, and ATP product stops.
To solve this trouble, cells convert NADH back into the election carrier, NAD+, through fermentation. This allows glycolysis to go on to produce ATP.
As with glycolysis, fermentation takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. There are two unlike forms of fermentation—lactic acid fermentation andalcoholic fermentation. Let'south first take a look at lactic acrid fermentation.
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Virtually organisms comport out fermentation through a chemical reaction that converts the pyruvate from glycolysis into lactic acid or lactate. Lactic acid fermentation likewise converts NADH into NAD+ so that glycolysis tin can continue.
The following diagram shows a summary of lactic acid fermentation.
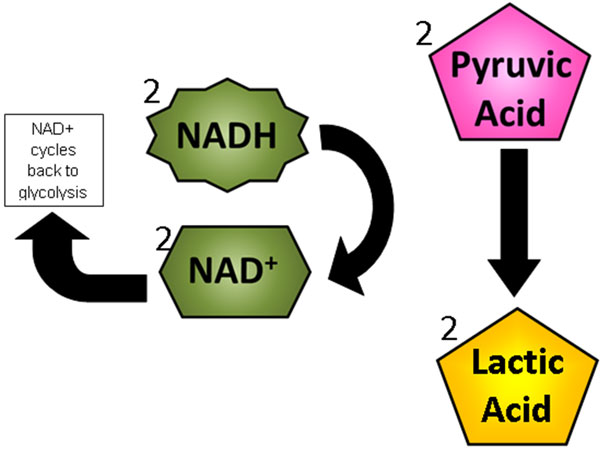
Humans undergo lactic acrid fermentation when the torso needs a lot of energy in a hurry. When you are sprinting full speed, your cells will only have enough ATP stored in them to last a few seconds. In one case the stored ATP is used, your muscles will start producing ATP through lactic acid fermentation. Fermentation makes it possible for cells to continue generating ATP through glycolysis.
Lactic acrid is a byproduct of fermentation. Lactic acid will build upward in fermenting cells and eventually limit the amount of fermentation that can occur. The only manner to get rid of lactic acid is through a chemical pathway that requires oxygen. As a result, after a quick dart, a runner will need to supply oxygen to cells with plenty of heavy breathing. An intense endeavour that lasts just a few seconds may require several minutes of heavy animate to deliver enough oxygen to cells to articulate the lactic acid build up.
| Many leaner are also lactic acrid fermenters. For example, bacteria used in the production of cheese, yogurt, buttermilk, sour cream, and pickles are lactic acid fermenters. Yogurt and cheese both outset with a source of sugar (i.eastward., lactose from milk). Then certain bacteria are added (e.g., Lactobacillus ). The leaner behave out lactic acid fermentation in the absence of oxygen. The bacteria catechumen the lactose carbohydrate to glucose, which enters glycolysis and is followed by lactic acid fermentation. Many other pathogenic microorganisms are killed west hen the acidity rises due to lactic acid build up . Lactic acid too imparts a abrupt, sour flavor typically associated with yogurt and sour cream. |  |
Cite Source
Renee Comet. A Giant brand yogurt container of apparently yogurt. Retrieved from https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Yogurt_(1).jpg
Alcoholic Fermentation
Yeast (a microscopic fungus) are as well capable of both cellular respiration and fermentation. When yeast cells are kept in an anaerobic environment (i.east., without oxygen), they switch to alcoholic fermentation to generate usable energy from food. Similar lactic acid fermentation, alcoholic fermentation generates NAD+ so that glycolysis can continue to produce ATP. Still, alcoholic fermentation in yeast produces ethyl alcohol instead of lactic acid as a waste material product. Alcoholic fermentation as well releases carbon dioxide.
The diagram below shows a summary of alcoholic fermentation.
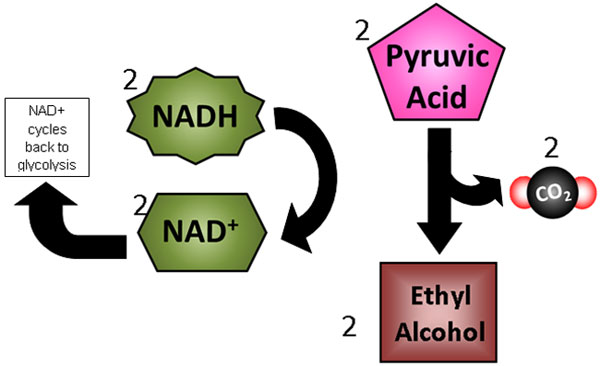
Alcoholic fermentation is the procedure that causes breadstuff dough to rise. When yeast cells in the dough run out of oxygen, the dough begins to ferment, giving off tiny bubbles of carbon dioxide. These bubbles are the air spaces yous come across in a slice of staff of life. The small amount of ethyl alcohol that is produced in the dough evaporates when the bread is baked.
Directions: Watch Bread Time Lapse to see the results of fermenting yeast cells producing carbon dioxide.
Source
Steven McCann. Bread Time Lapse. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vrKA4TYngFk&characteristic=youtu.be
Fermentation Review
Let'due south review the processes of fermentation. Here are some key points:
- Fermentation happens in anaerobic weather condition (i.e.,without oxygen).
- Fermentation begins with glycolysis which breaks down glucose into two pyruvate molecules and produces 2 ATP (net) and ii NADH.
- Fermentation allows glucose to be continuously cleaved down to make ATP due to the recycling of NADH to NAD+. (Without fermentation, the electron carrier would be full of electrons, the entire process would support, and no ATP would be produced.)
- Lactic acid (i.e., lactate) fermentation occurs in some strains of bacteria and in skeletal muscle and produces lactic acrid (i.e., lactate).
- Alcoholic fermentation occurs in yeast and produces ethanol and carbon dioxide.
- Fermentation only produces two ATP per glucose molecule through glycolysis, which is much less ATP than cellular respiration.
Journal Activeness
hornbergeraffen1947.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.texasgateway.org/resource/cell-processes-fermentation
0 Response to "when a cell does not have an electron transport chain, it uses fermentation to do what?"
Postar um comentário